If you love classical music, you likely know the violin. This lovely instrument is famed for its sweet singing tone and has charmed composers across the ages.
But have you ever stopped to wonder who invented the violin?

The origins of this beloved instrument are shrouded in mystery, but historians have been able to piece together some of its fascinating history.
From its humble beginnings as a simple wooden box with strings to its current status as a beloved symbol of classical music, the violin has captured the imaginations of musicians and music lovers for centuries.
Whether you’re a budding musician or just curious about the history of the violin, join me as we explore the exciting world of the violin!
Origins of the Violin

Have you ever wondered where the violin came from?
The violin’s origins can be traced back to the Middle Ages, when its predecessors, such as the viol, the rebec, and the vielle, were the most famous from across Europe and the Middle East.
In the fifteenth century, the violin began to take shape in Northern Italy, where it was known as the lira da braccio.
It was a bowed instrument with four strings and a carved back, and it quickly gained popularity among musicians and composers.
The lira da braccio was not the only bowed string instrument of its time.
The rebec, for example, was a popular instrument in the Iberian Peninsula, while the ravanastron was used in India and the Arabian rabab in the Middle East.
However, the lira da braccio evolved into the modern-day violin.
In the sixteenth century, Italian violin makers, such as Andrea Amati, Gasparo da Salò, and Giovanni Paolo Maggini, refined the instrument’s design and improved its sound quality.
By the seventeenth century, the violin had become the most popular bowed instrument in Europe, with famous composers such as Vivaldi, Bach, and Handel writing music specifically for it.
Today, the violin is played worldwide and has become integral to many different musical genres, from classical to folk to rock.
Its versatility and unique sound make it one of the most beloved musical instruments anywhere in the world.
The Amati Family and the Birth of the Modern Violin

The Amati family is one of the most influential families in violin-making history.
They played a crucial role in developing the modern violin, and their instruments are still highly regarded today.
Let’s take a closer look at the two most important members of the Amati family: Andrea Amati and Nicolo Amati.
Andrea Amati
Andrea Amati was born in Cremona, Italy, around 1505. He’s widely regarded as the inventor of the modern violin.
Andrea Amati designed and created the violin, viola, and cello, collectively called the “violin family.” He standardized these string instruments’ basic forms, shapes, sizes, materials, and construction methods.
Andrea Amati’s violins were highly sought after during his lifetime and are still considered some of the finest instruments ever made.
His instruments are known for their beautiful sound and exquisite craftsmanship. Andrea Amati’s work was so influential that it set the standard for violin-making for centuries.
Nicolo Amati
Nicolo Amati was the son of Girolamo Amati and was born in Cremona in 1596.
He was the most famous member of the Amati family and produced instruments notable for their beauty of workmanship and tone. Nicolo Amati was the master from whom Stradivari and Andrea Guarneri, among others, learned their craft.
Nicolo Amati’s violins are highly regarded for their sound quality and are considered some of the most beautiful instruments ever made.
His violins are known for their warm, rich, and complex tone, highly sought after by professional musicians and collectors alike.
Other Notable Violin Makers

Antonio Stradivari
Antonio Stradivari, born in Cremona, Italy in 1644, is regarded as the most excellent violin maker in history.
He began his career as a pupil of Nicolò Amati and created some of the most sought-after violins in the world.
Stradivari’s violins are known for their exceptional sound quality and beauty. His instruments are highly valued by musicians and collectors, with some selling for millions of dollars.

Andrea Guarneri
Andrea Guarneri was born in Cremona, Italy, in 1626 and was a contemporary of Antonio Stradivari.
Guarneri was known for his bold and powerful violins, which musicians highly sought after. His instruments are known for their rich, warm tone and exceptional playability.
Guarneri’s violins are also highly valued by collectors and have sold for millions of dollars.
Giuseppe Guarneri
Giuseppe Guarneri, also known as Guarneri del Gesù, was born in Cremona, Italy, in 1698. He was the son of another famous violin maker, Bartolomeo Giuseppe Guarneri.
Giuseppe Guarneri’s violins are known for their powerful, intense sound and are highly valued by musicians.
His instruments are also known for their unique and distinctive appearance, with many featuring ornate decorations and intricate designs.
Gasparo Da Salò
Gasparo Da Salò was born in Brescia, Italy, in 1540 and is considered one of the earliest and most famous violin makers.
His violins are known for their simple, elegant design and exceptional sound quality.
Gasparo’s contributions to the development of the stringed instrument are still recognized and celebrated today.
Giovanni Paolo Maggini
Giovanni Paolo Maggini was an Italian luthier who lived in the 16th and 17th centuries.
His violins, violas, and cellos are renowned for their deep, resonant sound and stunning craftsmanship.
Maggini’s instruments are highly sought after by musicians and collectors alike, and his legacy continues to influence the art of instrument-making.
Evolution of the
Violin Design
When you think of a violin, you probably imagine this iconic instrument’s classic, elegant, and curvy shape.
But did you know that the design of the violin has evolved, with various changes and modifications made to improve its sound quality, playability, and overall performance?
Let’s take a closer look at some of the key elements of the violin design and how they have evolved.
Originally, violins were played with a bow made from horsehair and a set of gut strings.
However, the materials used for strings and bows have evolved, with modern violins often using synthetic materials for strings and carbon fibre for bows.
The wood used to make violins has also changed over time. The most common woods used for violins are spruce and maple, with spruce used for the top and maple for the back, sides, and neck.
The neck of the violin has also undergone some changes, with modern violins often featuring an angled neck to improve playability.
The pegs and fingerboard are two parts of the violin that have remained relatively unchanged.
The pegs are used to tune the strings, while the fingerboard is where the musician presses down to the string to create different notes. Both of these components are typically made from ebony wood.
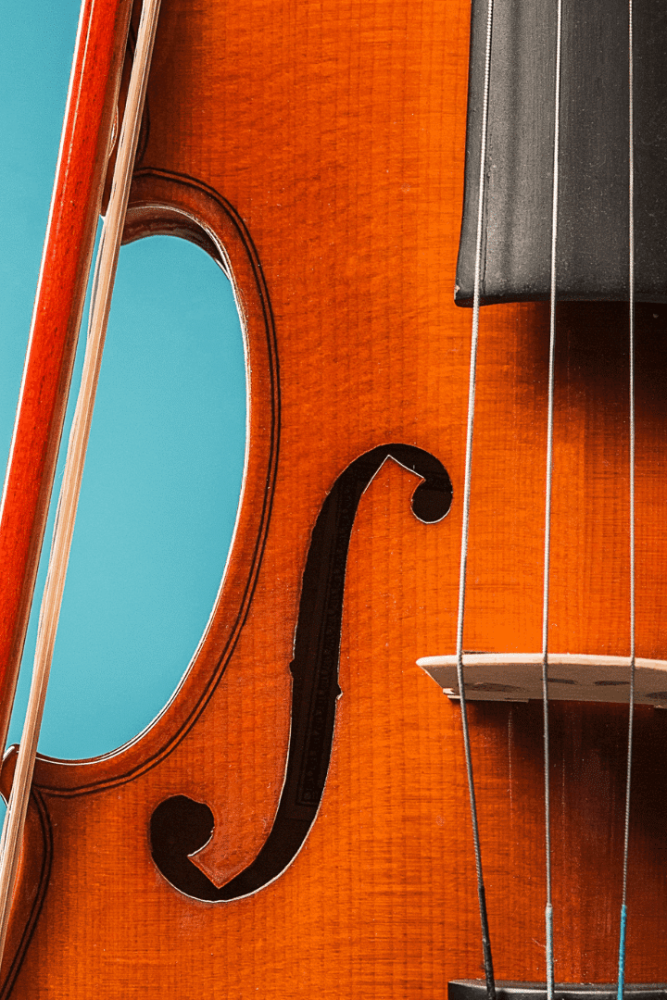
The f-holes and bass bar are two violin parts that significantly impact its sound quality.
The f-holes allow sound to escape from the violin, while the bass bar supports the top, helping amplify the sound.
These components have remained largely unchanged, with modern violins still featuring the same basic design.
The chin rest and tailpiece are two components that were added to the violin relatively recently.
The chin rest was first introduced in the early 1800s, while the tailpiece was added in the late 1800s.
The chin rest helps improve the musician’s comfort and stability, while the tailpiece holds the strings.
Unlike many stringed instruments, the violin has a fretless fingerboard, allowing greater flexibility and expressiveness in playing.
The violin’s bridge has also changed over time, with modern bridges often made from lighter materials to improve sound quality.

OUR RECOMMENDED VIOLINS
D Z Strad Model 220 Violin

FEATURES: Hand-carved solid spruce top
OTHER INFO: Includes boxwood pegs, tailpiece, and chinrest
- Beautiful tone and projection
- Comfortable playing for extended periods
- Comes with a case and bow
- More expensive than some other intermediate violins
When you click ‘Check Price’, you’ll see there are loads of great places to buy this item. Our personal favorite is Sweetwater for the US, and Thomann and Gear4Music for the UK & Europe.
They are the largest music retailers, with excellent customer service, competitive prices, really fast shipping, and the longest guarantees.
The professional musician who wrote this article combined many things,
from the product build, manufacturer’s reputation through to feedback
from other users, to create our famous TedScore™.
Yamaha AV7-44SG Student Violin Outfit

FEATURES: 4/4-size violin with a lightweight case, real Brazilwood bow, and Schwarz rosin
OTHER INFO: Spruce top and maple back/sides have been aged over five years for enhanced tonal richness and resonance
- Ebony tuning pegs, fingerboard, tailpiece, and chinrest
- Wittner Ultra tailpiece with four fine tuners
- Professionally adjusted and set up with premium Helicore strings
- String comes with a steel core, which can be upgraded to preferred strings
When you click ‘Check Price’, you’ll see there are loads of great places to buy this item. Our personal favorite is Sweetwater for the US, and Thomann and Gear4Music for the UK & Europe.
They are the largest music retailers, with excellent customer service, competitive prices, really fast shipping, and the longest guarantees.
The professional musician who wrote this article combined many things,
from the product build, manufacturer’s reputation through to feedback
from other users, to create our famous TedScore™.
Yamaha SV-200 Silent Electric Violin
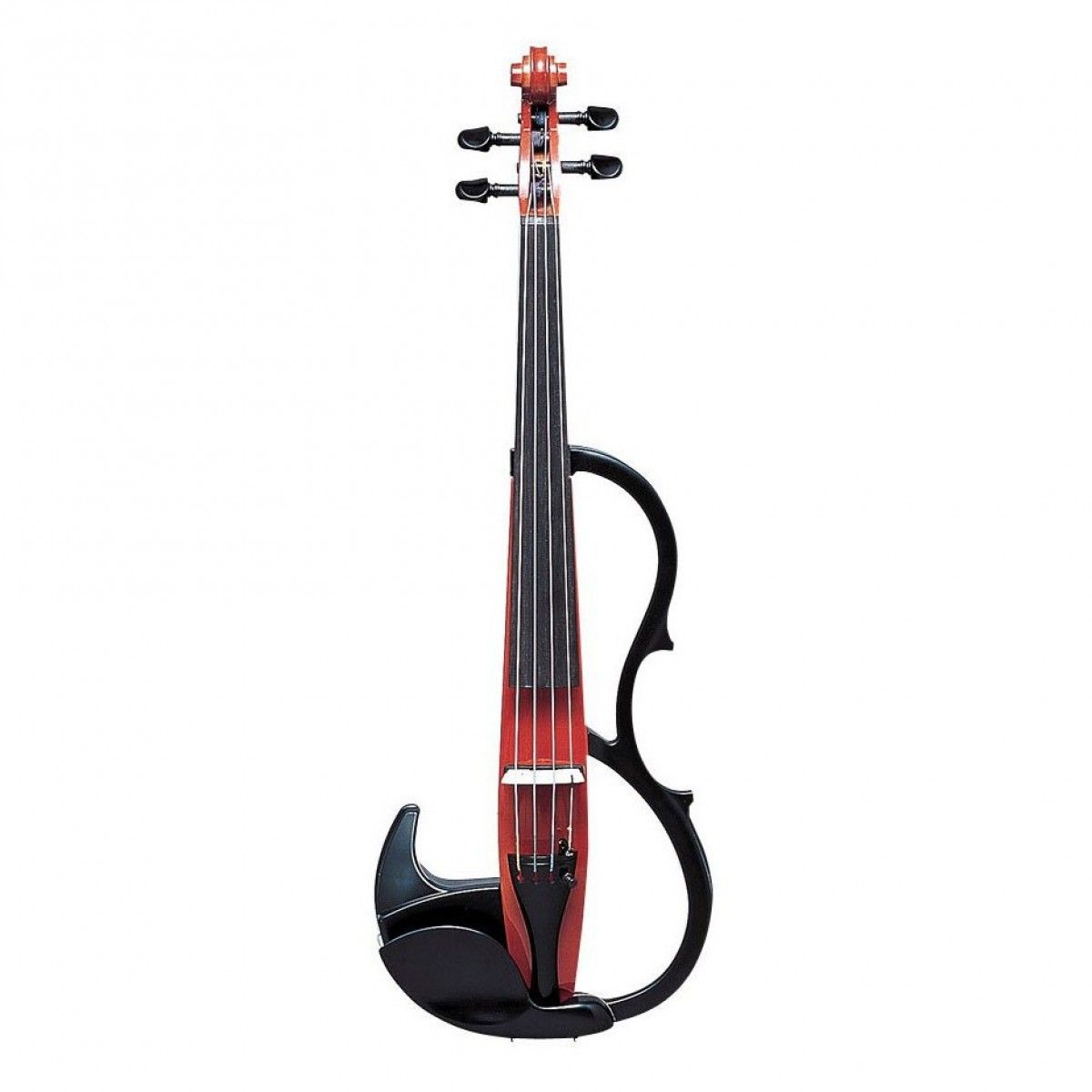

FEATURES: Solid spruce body
OTHER INFO: built with a high-quality pickup and preamp system
- Available in a different colour
- Versatile sound and performance options
- Lightweight design
- It may require additional equipment
When you click ‘Check Price’, you’ll see there are loads of great places to buy this item. Our personal favorite is Sweetwater for the US, and Thomann and Gear4Music for the UK & Europe.
They are the largest music retailers, with excellent customer service, competitive prices, really fast shipping, and the longest guarantees.
The professional musician who wrote this article combined many things,
from the product build, manufacturer’s reputation through to feedback
from other users, to create our famous TedScore™.
Who Invented The Violin
Summary
If you’re wondering who invented the violin, the answer is not entirely clear.
While Andrea Amati is often credited with inventing the violin, some historians debate whether he was the creator or simply the best-recorded violin maker of his time.
The violin’s singing tone was recognized early on in Italy, and some of the earliest makers had settled on its proportions by the end of the 16th century.
While we may never know for sure who invented the instrument, we can appreciate the incredible craftsmanship and artistry that have gone into creating and perfecting it over the centuries!
Before you go…
Don’t miss out on the chance to unleash your inner rockstar with our beginner violins!
Whether you’re into violin music, dreaming of playing classical music or jamming to your favorite pop songs, these 16 Violins For Beginners are the perfect starting point for your musical journey!
FAQ's
The violin was first invented in the early 16th century in Italy. Its origins are unclear, but it’s believed to have evolved from earlier stringed instruments such as the rebec and the lira da braccio.
The violin originated in northern Italy, specifically in Lombardy and Piedmont, in the early 16th century. It’s believed to have evolved from earlier stringed instruments that were popular in the region.
The exact reason for the invention of the violin is unknown, but it’s believed to have been created to improve upon earlier stringed instruments such as the rebec and the lira da braccio.
The violin’s unique design allowed for greater range, versatility, and expressiveness, making it a popular instrument for both classical and popular music.
The choice between a traditional and electric violin largely depends on the individual musician’s preference and style.
While traditional violins offer a classic, warm sound, electric violins can provide a unique, modern sound and greater versatility in effects and amplification.










I’m kinda new to all this violin stuff, but I’m really curious, like, how do you tell one violin maker’s work from another? Are there like specific things to look for that says ‘this is a Stradivari’ or ‘this was made by Nicolo Amati’? It’s all pretty confusing to me but also super interesting. Would love to get some pointers on this. Thanks for the great article, Reg , it’s opened up a whole new world for me!
Gasparo Da Salò often doesn’t get enough credit for his role in the evolution of the violin. While Amati and Stradivari are household names, Da Salò’s work in the 16th century laid important groundwork for what the instrument would become. His broad body of work influenced the Brescian school of violin making significantly.
Couldn’t agree more! Da Salò’s contributions are indeed unsung.
So, the Amati’s made violins cool before Stradivari made them hot? Guess every band needs a good opening act, even in the violin world!
Fascinating to read about the Amati family’s significant contributions to the modern violin. Their legacy in crafting violins that not only set the standard in build quality but also in sound excellence is truly remarkable. I’ve always been intrigued by how subtle changes in design can drastically alter a violin’s tone. It’s a gentle reminder of the deep connection between craftsmanship and artistry in the world of classical music. Reg , your deep dive into this subject is greatly appreciated!
Does anyone know if violins made by the Amati family are still playable today? It would be an experience to hear one live.